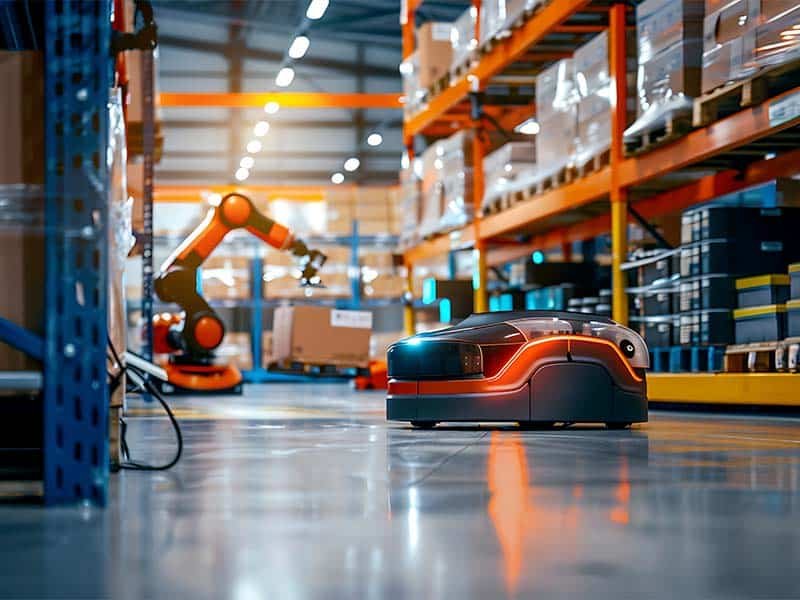
AGV Material Handling: Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) have become a cornerstone in modern material handling systems. As industries strive for increased efficiency, safety, and cost savings, AGV material handling solutions are rapidly transforming warehouses, manufacturing plants, and distribution centers worldwide. This article explores how AGVs work, their benefits, key types, and how to choose the right AGV system for your material handling needs.
If you’re considering upgrading your facility’s logistics or simply want to understand how AGV material handling can improve operational workflows, this comprehensive guide covers everything you need to know.
What Is AGV Material Handling?
AGV material handling refers to the use of Automated Guided Vehicles—robotic systems that transport materials within a facility without human intervention. These vehicles navigate via embedded wires, laser guidance, or advanced mapping software to move pallets, containers, and products from one point to another.
Unlike traditional forklifts or manual labor, AGVs operate autonomously, following pre-programmed routes or dynamic paths while interacting with other automated systems.
Key Components of AGV Systems:
- Vehicle platform (forklift, cart, tow tractor)
- Navigation system (laser, magnetic tape, GPS)
- Control software and communication modules
- Safety sensors and obstacle detection
How AGVs Improve Material Handling Operations
Integrating AGVs into material handling transforms the workflow in many positive ways:
1. Enhanced Efficiency and Productivity
AGVs operate 24/7 without breaks or fatigue, increasing throughput significantly. Automated transport reduces delays between production stages or shipping docks, optimizing inventory flow.
2. Increased Safety
Manual material handling involves risks like collisions, lifting injuries, and accidents. AGVs come equipped with sensors and emergency stop systems to detect obstacles and prevent collisions, making workplaces safer.
3. Cost Savings
While the upfront investment in AGV material handling systems can be substantial, the long-term savings on labor costs, accident-related expenses, and inventory losses often outweigh initial costs.
4. Consistent Accuracy
AGVs follow exact routes and schedules, reducing errors in material placement or inventory handling and improving overall operational accuracy.
Types of AGVs Used in Material Handling
Different facilities require different types of AGVs depending on their material handling needs. Here are some common AGV types:
1. Unit Load AGVs
Designed to move pallets or large containers, unit load AGVs are equipped with forks or conveyors. They are commonly used in warehouses and distribution centers.
2. Tow AGVs
These AGVs pull carts or trailers loaded with materials. Ideal for manufacturing plants or distribution hubs, tow AGVs replace traditional tugger trains.
3. Forklift AGVs
These are autonomous forklifts capable of picking up, transporting, and stacking pallets. They combine traditional forklift capabilities with autonomous navigation.
4. Assembly Line AGVs
Specialized for assembly operations, these AGVs deliver parts to workstations on a precise schedule, supporting just-in-time manufacturing.
5. Hybrid AGVs
Some systems combine multiple functionalities or navigation types for flexibility in complex environments.
Navigating the Different AGV Navigation Technologies
Understanding AGV navigation is critical to selecting the right AGV material handling system. Common navigation methods include:
- Magnetic Tape or Wire Guidance: Uses embedded wires or tape on the floor to guide AGVs along fixed paths.
- Laser Guidance: Employs reflectors placed around the facility and laser sensors on the vehicle for flexible, dynamic navigation.
- Inertial Navigation: Uses gyroscopes and accelerometers combined with map data to navigate without physical guides.
- Vision-Based Navigation: Cameras and computer vision software allow AGVs to interpret their surroundings and adapt routes dynamically.
- GPS Navigation: Primarily used in large outdoor yards or open environments.
Each method varies in cost, flexibility, and accuracy, influencing the overall performance of your material handling system.
Benefits of Implementing AGV Material Handling Systems
Investing in AGV material handling can provide numerous advantages, especially for facilities seeking scalability and modernization:
- Reduced Labor Costs: AGVs perform repetitive transport tasks, freeing workers for higher-value jobs.
- Operational Flexibility: Modern AGVs can be reprogrammed to accommodate layout changes or new workflows.
- Improved Inventory Management: Real-time tracking and predictable transport enhance inventory accuracy.
- Lower Maintenance Costs: AGVs require less maintenance compared to combustion forklifts.
- Sustainability: Electric-powered AGVs reduce carbon footprints and noise pollution.
Key Considerations When Choosing AGV Material Handling Solutions
Before adopting an AGV system, evaluate the following factors to ensure it meets your operational goals:
Facility Layout and Size
Complex layouts may require advanced navigation technologies like laser or vision-based AGVs for flexibility.
Load Types and Weights
Match AGV types to the materials you handle—heavy pallets, small packages, or assembly parts.
Integration with Existing Systems
Ensure your AGV system can communicate with warehouse management software (WMS) or manufacturing execution systems (MES).
Budget and ROI
Consider total cost of ownership, including installation, training, and ongoing maintenance.
Safety Regulations
Check compliance with industry safety standards and certifications to protect your workforce.
Case Studies: AGV Material Handling in Action
Automotive Industry
Leading car manufacturers use AGVs to transport parts across assembly lines, reducing downtime and improving production efficiency.
E-commerce Fulfillment
Warehouses utilize AGVs to speed up order picking and packing, meeting the rising demand for faster deliveries.
Food and Beverage
Temperature-controlled AGVs handle perishable goods with precision, maintaining quality and reducing waste.
Challenges and Future Trends in AGV Material Handling
While AGVs offer transformative benefits, there are challenges:
- Initial costs and integration complexity
- Navigation issues in highly dynamic environments
- Need for ongoing system updates and maintenance
Looking ahead, trends like artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and the Internet of Things (IoT) are enhancing AGV capabilities. Smart AGVs will better understand complex environments, collaborate with humans, and optimize routes autonomously.
Summary Table: AGV Material Handling Types and Uses
| AGV Type | Common Applications | Load Capacity | Navigation Method |
| Unit Load AGVs | Pallet transport in warehouses | Up to several tons | Magnetic tape, laser |
| Tow AGVs | Pull carts in manufacturing | Varies by trailer size | Laser, inertial |
| Forklift AGVs | Stacking and lifting pallets | Heavy-duty forklifts | Laser, vision-based |
| Assembly Line AGVs | Parts delivery in production | Lightweight to medium | Inertial, vision-based |
| Hybrid AGVs | Multi-purpose, flexible tasks | Variable | Mixed navigation systems |
Conclusion
AGV material handling is revolutionizing the way industries manage internal logistics. By automating the transport of materials, companies gain efficiency, improve safety, and reduce operational costs. Whether you operate a large warehouse, manufacturing plant, or distribution center, investing in AGV technology can future-proof your operations.
When selecting an AGV system, consider your unique needs—load type, facility layout, and integration capabilities—to maximize the benefits. As technology advances, AGVs will become even smarter and more adaptable, solidifying their role in the future of material handling.
Are you ready to transform your facility with AGV material handling? Exploring the right system now can put your business ahead in automation and efficiency.